Practice Aptitude tests guide
What is an aptitude test and what does it measure?
Aptitude tests are designed to measure your work-related cognitive capacity. The concept behind these tests is that each test question has only one correct answer, and everyone can correctly solve all the test questions. The only difference between people is in how quickly they can correctly complete the test (i.e. answer all the test questions). That’s why these tests are always timed. The time is defined in such a way that only 1% to 5% of the population can correctly solve all the test questions within the allowed time frame.
What do aptitude tests measure? These tests measure what Psychometric test experts refer to as your fluid and crystallised intelligence. The theory of fluid and crystallised intelligence suggests that people’s intelligence is composed of a number of different abilities that interact and work together to produce overall individual intelligence.
Fluid intelligence is the ability to think and reason abstractly and solve problems. It’s more commonly known as ‘street smarts’ or the ability to ‘quickly think on your feet’ . This ability is considered independent of learning, past experience, and education. Examples of the use of fluid intelligence include coming up with problem-solving strategies, ability to quickly learn new skills, ability to quickly integrate new information, strategic thinking, etc. The aptitude test that measures your fluid intelligence is called abstract reasoning.
The second component of intelligence that the aptitude tests measure is crystallised intelligence. Crystallised intelligence is the ability to learn from past experiences and relevant learning, and to apply this learning to a situation. Employers, obviously, will only be interested in your ability to apply your learnings to work-related situations. Work situations that require crystallised intelligence include comprehending written reports and instructions, ability to produce reports, ability to use numbers as a tool to make effective decisions, etc. This type of intelligence is based upon facts and rooted in experiences, and becomes stronger as we age and accumulate new knowledge and understanding. There are many aptitude tests that measure different aspects of crystallised intelligence. The most common are verbal reasoning, numerical reasoning, spatial reasoning and mechanical reasoning
Popular aptitude tests and what to expect in each aptitude test
One aptitude test name but many test question styles
It is very important to understand that while aptitude test names are generic, the test questions styles in the test are very specific for the job. For example, two candidates will have a numerical reasoning test but the one applying for the Defence Force will have very different style of test questions than the one applying for investment banking. Therefore, it is very important to ensure that you prepare for the style of test questions that you will have in your real test.
Abstract reasoning or Inductive reasoning
Also called conceptual reasoning, this test is unique in its design. It is a non-verbal test, which uses shapes rather than words or text to measure someone’s fluid intelligence. Each test question includes a series of shapes with common logical rules. Your fluid intelligence is measured by the number of correct answers (i.e. correct identification of the shapes’ logical rules) within the given time. Read more about the abstract reasoning test
Example abstract or inductive reasoning test question:
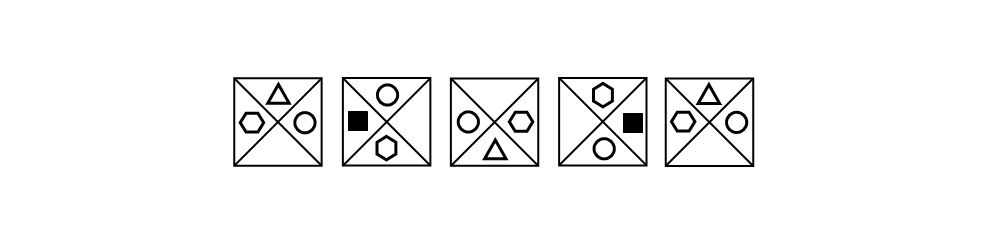 What is the next shape?
What is the next shape?
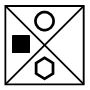
To answer this test question, we need to first identify the patterns and logical rules that are relevant to the group of shapes in the test question. In this series, there are two logical rules moving left to right. The first is that all the inner shapes move one place anticlockwise at each step. The second rule is that, at every step, the triangle alternates with a black square. At step five, there is a triangle at the top – therefore, at the next step, it will move anticlockwise into the left place and become a black square. See below the correct answer:
Verbal reasoning test or verbal aptitude test
This is a timed test that is designed to measure your verbal analytical skills (or verbal reasoning skills). These skills include the capacity to quickly identify critical issues from written material such as reports, and logically derive conclusions from written facts or data. If, for example, you can process written documents and can come up with the most important content fairly quickly, then there is a good chance that you have high verbal reasoning skills. Read more about the verbal reasoning test
There are several styles of verbal reasoning test questions. The most common one is a reading comprehension verbal test question. Please read an example of this style of verbal test questions:
Please read the following passage and answer the question at the end of the passage:
Dear Employee:
You have completed another year with the company, and you have continued to do a very good job overall. Your punctuality, professional demeanour, and attention to detail all continue to be at a very high level.
There are, however, a few aspects of your job performance that need improvement. First, as a regular daily occurrence at practices, you often fail to gather the balls and put them back on their racks in a timely enough fashion; our players want those balls back on the racks as soon as possible so that they can continue practicing without delays and without losing their rhythm. Second, water needs to be available to any player at any time and, occasionally, you have been slow to get water to the players as soon as they come off the court. Be sure to have the water ready for a player as soon as it is needed. Finally, you should always be available to immediately retrieve balls that bounce away from the court. Recently, after one player shot an air-ball, you didn’t retrieve the ball until after free-throw shooting drills had begun. Please make a point to retrieve balls as quickly as possible.
Question:
The employee has done a great job in the past year in terms of making water available.
Based on the passage, is this statement:
True
False
or Can't say?
To answer this question, we need to read the passage. The report’s second point states that the employee needs to do a better job in water availability. Therefore, the correct answer is 'False'.
Deductive reasoning test
The deductive reasoning test is a timed test that is designed to measure your ability to read a passage and logically deduct based on the information provided. A deduction skill is required in most companies and organisation, as it ensures that you read information and draw correct conclusions based on the facts given. Read more about the Deductive reasoning test
An example of a deductive reasoning test question:
Which two statements together prove that Tim has a red car?
A. Gil likes Tim's car colour
B. Tim likes fast cars
C. Gil has a fast car
D. Gil likes only red cars
E. Tim's car is not silver
To answer this verbal test question, we need to first examine what each statement says. If we take statement A ‘Gil likes Tim’s car colour’ and combine it with statement D ‘Gil likes only red cars’ then those alone prove that Tim has a red car. The logic is that if Gil likes only red cars (D) and he likes Tim’s car colour (A) then Tim’s car must be red.
Numerical reasoning test or numerical aptitude test
This test is also a timed test. It measures your numerical analytical skills (or numerical reasoning skills).These skills include the capacity to quickly identify critical issues from numerical data such as graphs and tables. It also includes the capacity to use work-related numerical data such as performance figures or financial outcomes to make effective decisions. It is important to note that numerical reasoning skills don’ t measure your mathematical ability. Read more about the numerical reasoning test
There are several styles of numerical aptitude and numerical reasoning test questions.
Example of a numerical reasoning test which requires an interpretation of a table:
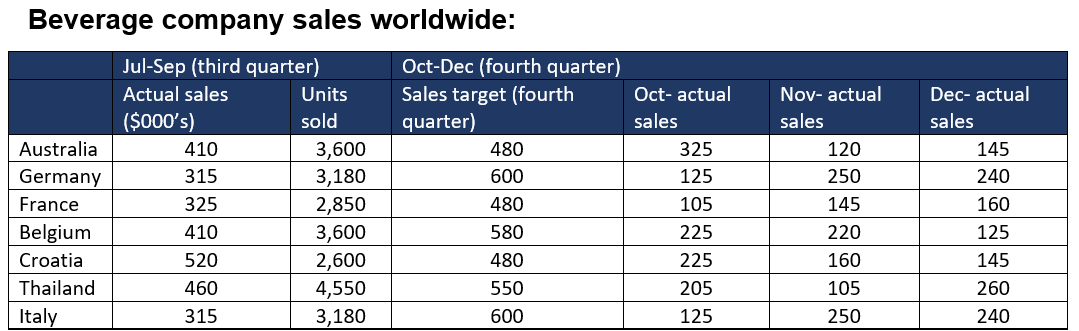
What is the ratio of the differences in actual sales to target sales in Thailand and Italy during the fourth quarter?
To answer this test question, we need to review the information provided in the table. According to the table, Thailand’s fourth-quarter sales target was 550, but actual sales were: 205 + 105 + 260 = 570. This is a difference of 20 (570 – 550). Italy’s target was 600 sales, but actual sales were: 125 + 250 + 240 = 615. The difference here was 15 (615 – 600). Therefore, the Thailand to Italy ratio of differences is 20:15 = 4:3.
Example of a numerical reasoning or numerical aptitude test which offers numerical information in text:
If Sharon had 3 more oranges, then she would have three-quarters of the number of oranges that Mark has. If Sharon gave away 3 oranges, then she would have half the number of oranges that Mark has.
How many oranges does Sharon have?
There are several ways to approach this question, probably the simplest way is to come up with two equations and two variables (one is Sharon’s number of oranges and the other is Mark’s number of oranges) representing the information provided in the question. Then when we solve the two equations we will find the answer to the question. Based on the first sentence in the question we can write the following equation: S + 3 = ¾ x M. S is the number of oranges Sharon has and M is the number of oranges Mark has. Based on the second sentence, we can write the second equation: S – 3 = ½ x M. To find what M and S are, we need to solve these two equations. If we subtract the second equation from the first one we can get what M is. S + 3 – (S -3) = ¾ x M – ½ x M or 6 = ¼ x M. This means that M = 6 x 4 = 24. Therefore, S = ½ x 24 +3 = 15.
Other aptitude tests that measure your crystallised intelligence but are less common:
Spatial reasoning
This timed test measures your ability to visually manipulate objects. This is used to measure your ability to efficiently organise a warehouse or any other type of space. It is also used to measure your ability to identify hazards in the workplace or to solve technical problems.
Mechanical reasoning
This timed test measures your ability to quickly comprehend mechanical concepts and solve mechanical problems.









